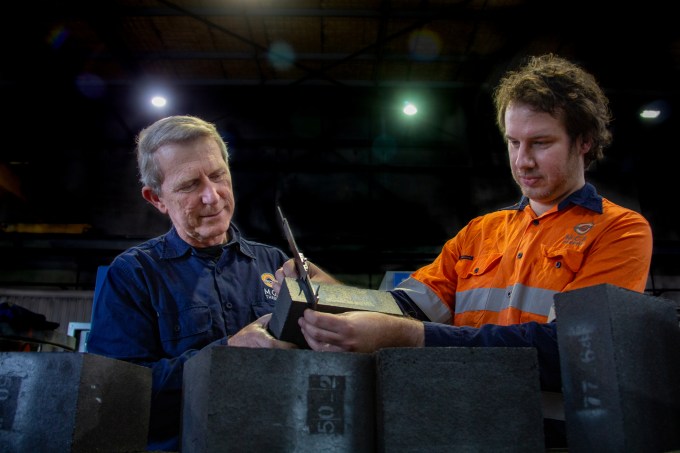
MGA Thermal co-founders Erich Kisi and Alex Post. Image Credits: MGA Thermal
MGA Thermal wants to help utility companies transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources with shoebox-sized thermal energy storage blocks. The company says a stack of 1,000 blocks is about the size of a small car and can store enough energy to power 27 homes for 24 hours. This gives utility providers the ability to store large amounts of energy and have it ready to dispatch even when weather conditions aren’t ideal for generating solar or wind power. The modular blocks also make it easier to convert infrastructure, like coal-fired power plants, into grid-scale energy storage.
MGA Thermal announced today it has raised $8 million AUD (about $5.9 million USD), bring its total funding so far to $9 million AUD. The round was led by Main Sequence, a venture firm founded by Australia’s national science agency that recently launched a new $250 million AUD fund. Alberts Impact Capital, New Zealand’s Climate Venture Capital Fund, The Melt and returning investor CP Ventures participated, along with angel investors like Chris Sang, Emlyn Scott and Glenn Butcher.
Based in Newcastle, Australia, MGA Thermal was founded in April 2019 by Erich Kisi and Alexander Post after nearly a decade spent researching and developing miscibility gap alloys technology at the University of Newcastle. When asked to explain MGA tech in layperson’s terms, Kisi used a delicious analogy.
MGA Thermal’s blocks “essentially comprise metal particles that melt when heated embedded in an inert matrix material. Think of a block as being like a choc-chip muffin heated in a microwave. The muffin consists of a cake component, which holds everything in shape when heated, and the choc chips, which melt,” he told TechCrunch.
“The energy that goes into melting the choc chips is stored and can burn your mouth when you bite into the muffin,” he added. “Melting energy is more intense than merely heating something up and that melting energy is concentrated near the melting temperature so energy can be released in a consistent way.”
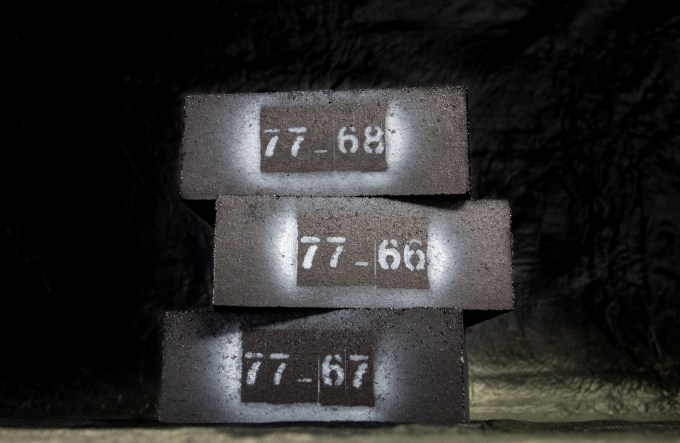

MGA Thermal’s modular energy storage blocks. Image Credits: MGA Thermal
Energy stored in MGA Thermal’s blocks can be used to heat water to power steam turbines and generators. In this scenario, blocks are designed with internal tubing for pumping and boiling water, or interact with a heat exchanger. Kisi said MGA Thermal’s blocks enable aging thermal power plans to continue running on renewable energy that would usually be switched off in situations like overheating caused by too much sun or high winds.
Other thermal energy solutions include heating low-cost solid materials in blocks or granules to high temperatures in an insulated container. But many of these materials aren’t good at moving thermal energy around and have temperature limitations, Kisi said. This means thermal energy decreases in temperature as it is discharged, making it less effective.
Another method for storing thermal energy involves molten salts that are heated by a renewable energy source and stored in a hot tank. The hot salt is then pumped through a heat exchanger to make steam, while colder (but still molten) salt is returned to a “cold” tank.
“These systems are widely used in concentrating solar thermal energy but have found little use elsewhere,” Kisi said. “That’s mostly because there is a large infrastructure cost for piping pumps and heaters, and a large amount of power is wasted keeping the salt from freezing.”
MGA Thermal is establishing a manufacturing plant in New South Wales to scale to commercial levels production of its blocks, and plans to double its team over the next 12 months so it can make hundreds of thousands of blocks each month. It is also currently working with partners like Swiss company E2S Power ASG and U.S.-based Peregrine Turbine Technologies to deploy its tech in Australia, Europe and North America. For example, E2S Power AG will use MGA Thermal’s tech to repurpose retired and active coal-fired thermal plants in Europe.
While MGA Thermal’s tech has many industrial use cases, like converting power stations, building off-grid storage and supplying power to remote communities and commercial spaces, it can also help consumers consume less fossil fuel. For example, MGA blocks can be used by households to store excess energy generated from rooftop solar panels or small wind turbines. Then that energy can be used to heat homes.
“Around the world an estimated three billion people heat their homes by burning fuel,” said Kisi. “That’s a lot of CO2, especially in very cold climates.”
In a statement, Main Sequence partner Martin Duursma said, “A core focus of our new fund is uncovering the scientific discoveries, and helping to turn them into real, tangible technologies so we can reverse our climate impact. Erich Kisi and Alexander Post’s impressive deep research backgrounds, their expert team and innovative technology are paving the way for grid-scale energy storage and boosting the capability of a renewable energy future globally.”

Source: Tech Crunch