Facebook’s role in the opioid crisis could become another scandal following yesterday’s release of harrowing new statistics from the Center for Disease Control. It estimated there were nearly 30,000 synthetic opioid overdose deaths in the U.S. in 2017, up from roughly 20,000 the year before. When recreational drugs like Xanax and OxyContin are adulterated with the more powerful synthetic opioid Fentanyl, the misdosage can prove fatal. Xanax, OxyContin and other pain killers are often bought online, with dealers promoting themselves on social media including Facebook.
Hours after the new stats were reported by The New York Times and others, a source spotted that Facebook’s internal search engine stopped returning posts, Pages and Groups for searches of “OxyContin,” “Xanax,” “Fentanyl” and other opioids, as well as other drugs like “LSD.” Only videos, often news reports deploring opiate abuse, and user profiles whose names match the searches, are now returned. This makes it significantly harder for potential buyers or addicts to connect with dealers through Facebook.
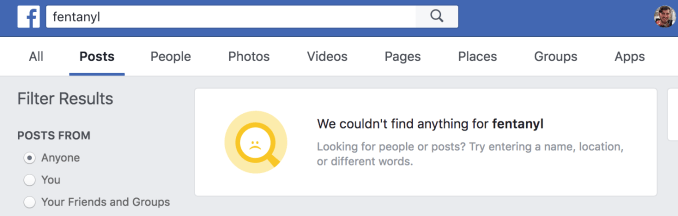
However, some dealers have taken to putting drug titles into their Facebook profile names, allowing accounts like “Fentanyl Kingpin Kilo” to continue showing up in search results. It’s not exactly clear when the search changes occurred.
On some search result pages for queries like “buy xanax,” Facebook is now showing a “Can we help?” box that says “If you or someone you know struggles with opioid misuse, we would like to help you find ways to get free and confidential treatment referrals, as well as information about substance use, prevention and recovery.” A “Get support” button opens the site of The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, a branch of the U.S. department of health and human services that provides addiction resources. Facebook had promised back in June that this feature was coming.
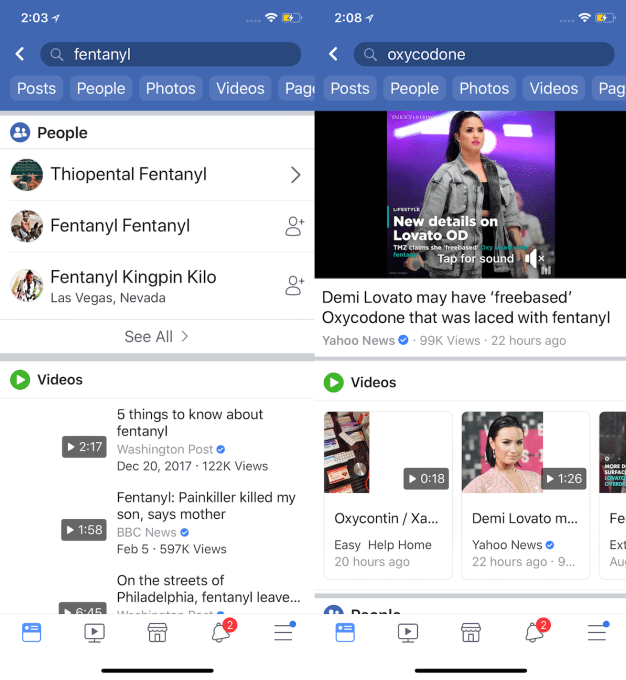
Facebook search results for many drug names now only surface people and video news reports, and no longer show posts, Pages or Groups, which often offered access to dealers
When asked, Facebook confirmed that it’s recently made it harder to find content that facilitates the sale of opioids on the social network. Facebook tells me it’s constantly updating its approach to thwart bad actors who look for new ways to bypass its safeguards. The company confirms it’s now removing content violating its drug policies, and it’s blocked hundreds of terms associated with drug sales from showing results other than links to news about drug abuse awareness. It’s also removed thousands of terms from being suggested as searches in its typeahead.

Prior to recent changes, buyers could easily search for drugs and find posts from dealers with phone numbers to contact
Regarding the “Can we help?” box, Facebook tells me this resource will be available on Instagram in the coming weeks, and it provided this statement:
We recently launched the “Get Help Feature” in our Facebook search function that directs people looking for help or attempting to purchase illegal substances to the SAMHSA national helpline. When people search for help with opioid misuse or attempt to buy opioids, they will be prompted with content at the top of the search results page that will ask them if they would like help finding free and confidential treatment referrals. This will then direct them to the SAMHSA National Helpline. We’ve partnered with the Substance Abuse & Mental Health Services Administration to identify these search terms and will continue to review and update to ensure we are showing this information at the most relevant times.
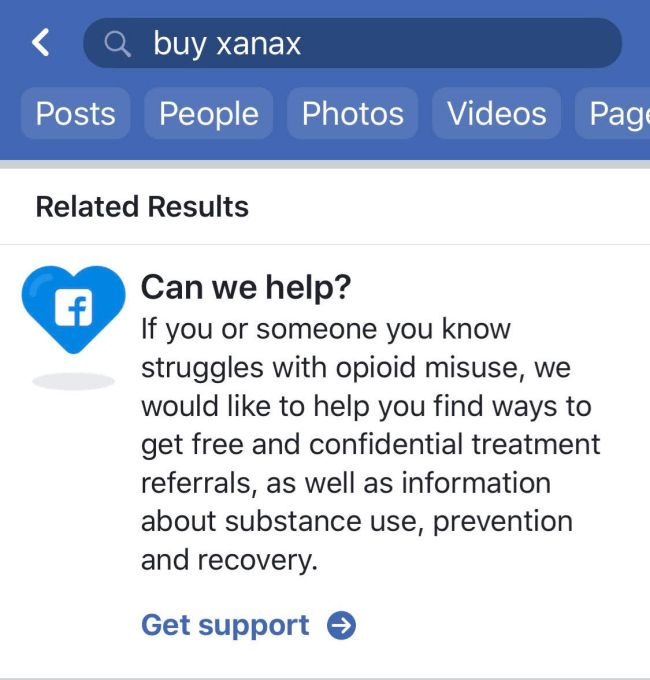
Facebook’s new drug abuse resource feature
The new actions follow Facebook shutting down some hashtags like “#Fentanyl” on Instagram back in April that could let buyers connect with dealers. That only came after activists like Glassbreakers’ Eileen Carey aggressively criticized the company, demanding change. In some cases, when users would report Facebook Groups’ or Pages’ posts as violating its policy prohibiting the sale of regulated goods like drugs, the posts would be removed, but Facebook would leave up the Pages. This mirrors some of the problems it’s had with Infowars around determining the threshold of posts inciting violence or harassing other users necessary to trigger a Page or profile suspension or deletion.

Facebook in some cases deleted posts selling drugs, but not the Pages or Groups carrying them
Before all these changes, users could find tons of vendors illegally selling opioids through posts, photos and Pages on Facebook and Instagram. Facebook also introduced a new ads policy last week requiring addiction treatment centers that want to market to potential patients be certified first to ensure they’re not actually dealers preying on addicts.
Much of the recent criticism facing Facebook has focused on it failing to prevent election interference, privacy scandals and the spread of fake news, plus how hours of browsing its feeds can impact well-being. But its negligence regarding illegal opioid sales has likely contributed to some of the 72,000 drug overdose deaths in America last year. It serves as another example of how Facebook’s fixation on the positive benefits of social networking blinded it to the harsh realities of how its service can be misused.
Last November, Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg said that learning of the depths of the opioid crisis was the “biggest surprise” from his listening tour visiting states across the U.S, and that it was “really saddening to see.”
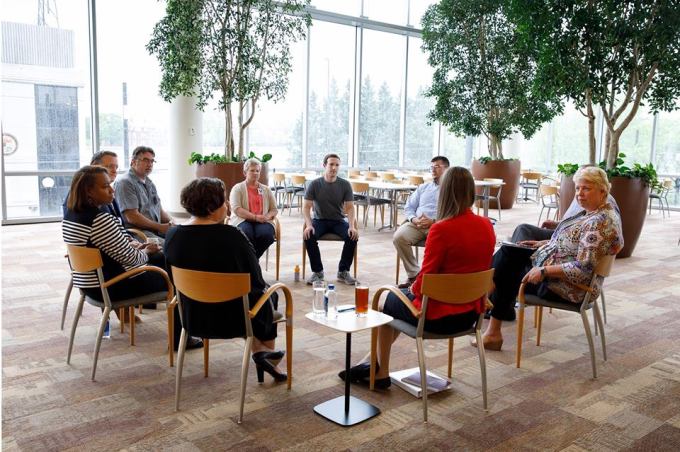

Zuckerberg meets with Opioid crisis caregivers and the families of victims in Ohio in April 2017
Five months later, Representative David B. McKinley (R-W.VA) grilled Zuckerberg about Facebook’s responsibility surrounding the crisis. “Your platform is still being used to circumvent the law and allow people to buy highly addictive drugs without a prescription” McKinley said during Zuckerberg’s congressional hearings in April. “With all due respect, Facebook is actually enabling an illegal activity, and in so doing, you are hurting people. Would you agree with that statement?” The CEO admitted “there are a number of areas of content that we need to do a better job policing on our service.”
Yet the fact that he called the crisis a “surprise” but failed to take stronger action when some of the drugs causing the epidemic were changing hands via his website is something Facebook hasn’t fully atoned for, nor done enough to stop. The new changes should be the start of a long road to recovery for Facebook itself.
Source: Tech Crunch

